Microsoft Office is an office suite of applications, servers, and services developed by Microsoft. It was first announced by Bill Gates on 1 August 1988, at COMDEX in Las Vegas. Initially a marketing term for a bundled set of applications, the first version of Office contained Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, and Microsoft PowerPoint. Over the years, Office applications have grown substantially closer with shared features such as a common spell checker, OLE data integration and Visual Basic for Applications scripting language. Microsoft also positions Office as a development platform for line-of-business software under the Office Business Applications brand. On 10 July 2012, Softpedia reported that Office is used by over a billion people worldwide.[5]
Office is produced in several versions targeted towards different end-users and computing environments. The original, and most widely used version, is the desktop version, available for PCs running the Windows and macOS operating systems. The most current desktop version is Office 2016 for Windows and macOS, released on 22 September 2015[6] and 9 July 2015,[7] respectively.
More recently, Microsoft developed Office Mobile, which are free-to-use versions of Office applications for mobile devices. Microsoft also produces and runs Office Online, a web-based version of core Office apps, which is included as part of a Microsoft account.
Contents [hide]
1 Desktop components
1.1 Word
1.2 Excel
1.3 PowerPoint
1.4 Access
1.5 Outlook
1.6 OneNote
1.7 Sway
1.8 Other desktop applications
1.9 Mobile apps
1.10 Server applications
1.11 Web services
2 Office Mobile
3 Common features
4 File formats and metadata
5 Extensibility
6 Password protection
7 Versions
7.1 Compatibility
7.2 Licensing
7.3 Support
8 Discontinued applications and features
8.1 Discontinued server applications
8.2 Discontinued web services
9 Criticism
10 Version history
10.1 Windows versions
10.2 Mac versions
11 References
12 External links
I will teach you MS. OFFIICE with pictures and videos. If you have still any Question you can freely ask me.
Lets start the from basic level. By Click the picture you can go to video session to watch the tutorial
BOLD
They are tools for emphasis. Bold and italic styles are designed to contrast with regular roman text, they’re somewhat harder to read. bold and italic are fine for short stretches of text, but not for long ones. The difference can be seen by above mentioned headings and their detail over here. You can apply them by selecting your desired words and then pressing the "B" , "I", "U" buttons as well.


Office is produced in several versions targeted towards different end-users and computing environments. The original, and most widely used version, is the desktop version, available for PCs running the Windows and macOS operating systems. The most current desktop version is Office 2016 for Windows and macOS, released on 22 September 2015[6] and 9 July 2015,[7] respectively.
More recently, Microsoft developed Office Mobile, which are free-to-use versions of Office applications for mobile devices. Microsoft also produces and runs Office Online, a web-based version of core Office apps, which is included as part of a Microsoft account.
Contents [hide]
1 Desktop components
1.1 Word
1.2 Excel
1.3 PowerPoint
1.4 Access
1.5 Outlook
1.6 OneNote
1.7 Sway
1.8 Other desktop applications
1.9 Mobile apps
1.10 Server applications
1.11 Web services
2 Office Mobile
3 Common features
4 File formats and metadata
5 Extensibility
6 Password protection
7 Versions
7.1 Compatibility
7.2 Licensing
7.3 Support
8 Discontinued applications and features
8.1 Discontinued server applications
8.2 Discontinued web services
9 Criticism
10 Version history
10.1 Windows versions
10.2 Mac versions
11 References
12 External links
I will teach you MS. OFFIICE with pictures and videos. If you have still any Question you can freely ask me.
Lets start the from basic level. By Click the picture you can go to video session to watch the tutorial
Office Button
Office button shows the file menu. When you click on mentioned place under the arrow a pop down menu oppens. It contains the following list
- New
- Open
- Save
- Save as
- Closs
New
These or the most important topics than other in pop down. these will be discus in later tutorial.
Click on New Button or Press the Short key which is (ctrl+n), a new blank page opens. This page shows Rows and Column. In row's Direction address is mentioned with alphabetical and toward column address is mentioned by no. When some one is want to tell about selected cell, he will tell that that is "A1" cell and so on. By telling adress of the cell first of all alphabetic and then numeric is told.
Open
Open button is to open the saved file in the computer or networking. When someone clicks on open button a box is opened like picture given bellow
After opening the required file you can edit it and can make your desire changes.
SAVE/SAVE AS
The next step is to save the file, if you save the file then opened file will be changed as it is but you can not find the previous file which was presented in computer. For example i want that my changes must not affect my saved file then i will click the " save as " button which is shown in first picture.
There is difference b/w "save" save as" in "save" your opened file become edited but in " save as " option you get a new file and you previous file remain unchanged. Short key for " save" is (ctrl+s) but short key for " save as " is ( f12) button.
PRINT (CTRL+P)
After making all changes and saving the file you can print you desired file. The question is! how can i print my file and how it will be after print ? This is very important thing because when the newcomers in job field go to an interview and asked to print the file they remain fail to accurate print.
VIDEO TUTORIAL
FONTS FORMATE

FONTS
Fonts are the main part in ms office. Fonts formate contains following features:
- Bold (CTRL+B)
- ITALIC (CTRL+I)
- UNDERLINE (CTRL+U)
- FONT COLOR
- FONT SIZE
- FONT STYLE
- SUBSCRIP/UNDER SCRIPT/
BOLD
They are tools for emphasis. Bold and italic styles are designed to contrast with regular roman text, they’re somewhat harder to read. bold and italic are fine for short stretches of text, but not for long ones. The difference can be seen by above mentioned headings and their detail over here. You can apply them by selecting your desired words and then pressing the "B" , "I", "U" buttons as well.
FONTS COLOR
You can change the color of text in your Word document.
- Select the text that you want to change.
- On the Home tab, in the Font group, choose the arrow next to Font Color, and then select a color.
 You can also use the formatting options on the Mini toolbar to quickly format text. The Mini toolbar appears automatically when you select text.
You can also use the formatting options on the Mini toolbar to quickly format text. The Mini toolbar appears automatically when you select text.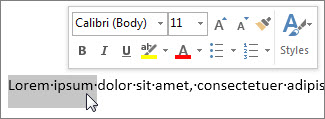
CHANGE OF FONT SIZE
Change the size of selected text
To change the font size of selected text in desktop Excel:
- Select the text or cells with text you want to change. To select all text in a Word document, press Ctrl + A.
- On the Home tab, click the font size in the Font Size box.
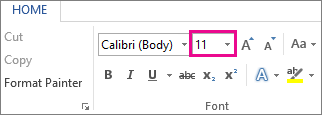 You can also type in any size you want, within the following limits:
You can also type in any size you want, within the following limits: - Excel: between 1 and 409, between 1 and 409, in multiples of .5 (such as 10.5 or 105.5)
CHANGE OF FONT STYLE
Change the font style or size for a worksheet
Want a different font style or size for your entire worksheet? Here’s how you can apply another font style or size:
- Click the first cell in the worksheet (cell A1).
- Press Ctrl+Spacebar, and then press Shift+Spacebar.
- Click the arrow next to the font name and pick another font.

- To change the font size, click the arrow next to the font size and pick another size.Tip: If you don’t like the changes you made, you can click Undo to return to the previous font style or size
SUBSCRIP/UNDER SCRIPT

A subscript or superscript is a character (number, letter or symbol) that is (respectively) set slightly below or above the normal line of type. It is usually smaller than the rest of the text. Subscripts appear at or below the baseline, while superscripts are above. Subscripts and superscripts are perhaps most often used in formulas, mathematical expressions, and specifications of chemical compounds and isotopes, but have many other uses as well.
In professional typography, subscript and superscript characters are not simply ordinary characters reduced in size; to keep them visually consistent with the rest of the font, typeface designers make them slightly heavier[clarification needed] than a reduced-size character would be. The vertical distance that sub- or superscripted text is moved from the original baseline varies by typeface and by use.
In typesetting, such types are traditionally called "superior" and "inferior" letters, figures, etc., or just "superiors" and "inferiors". In English, most nontechnical use of superiors is archaic.[1] Superior and inferior figures on the baseline are used for fractions and most other purposes, while lowered inferior figures are needed for chemical and mathematical subscripts.[2]
Superscript
Superscript and subscript refer to numbers that are positioned slightly higher or slightly lower than the text on the line. For example, chemical formulas use subscript (H2O), and an exponent is often formatted as a superscript (X4).

Make text subscript or superscript
- Select the text that you want to format as subscript or superscript.
- Do one of the following:
- On the Home tab, in the Font group, click Subscript. Or press CTRL+=.
Note: Keyboard shortcuts do not work if you are using Word Online.
To undo the formatting, click the Subscript or Superscript button again, or repeat the keyboard shortcut.